He used the data to spot trends over the years and understand his colonies' health and economic viability. A longitudinal study is a study that observes a subject or subjects over an extended period of time. When talking about what is a longitudinal study, we cannot go without also discussing the types of longitudinal research design.

Craft Beautiful Surveys
Retrospective studies are generally less expensive and take less time than prospective studies, but they are more prone to measurement error. For example, familiarity with test items and procedures may allow participants to improve their scores over repeated testing above and beyond any true change. Cohort effects can also interfere with estimating other effects like retest effects. This happens because comparing groups to estimate retest effects relies on cohort equivalence. It is important to minimize attrition by tracking participants, keeping contact info up to date, engaging them, and providing incentives over time. This tendency is known as selective attrition and can threaten the validity of an experiment.
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Qualitative longitudinal research in health research: a method study - BMC Medical Research Methodology - BMC Medical Research Methodology
Qualitative longitudinal research in health research: a method study - BMC Medical Research Methodology.
Posted: Sat, 01 Oct 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
A longitudinal study follows what happens to selected variables over an extended time. Psychologists use the longitudinal study design to explore possible relationships among variables in the same group of individuals over an extended period. Started in 2006, Growing Up In Ireland is a longitudinal study conducted by the Irish government to understand what children’s life looks like in different age brackets. The long-term study can yield interesting results by following a set of children throughout their childhood.
Common errors

Many medical studies are longitudinal; researchers note and collect data from the same subjects over what can be many years. Longitudinal methods may provide a more comprehensive approach to research, that allows an understanding of the degree and direction of change over time. Longitudinal data collection is the process of gathering information from the same sample population over a long period. Longitudinal data collection uses interviews, surveys, and observation to collect the required information from research sources.
Time invested in this initial period will improve the accuracy of data eventually received, and contribute to the validity of the results. Regular monitoring of outcome measures, and focused review of any areas of concern is essential (3). These studies are dynamic, and necessitate regular updating of procedures and retraining of contributors, as dictated by events. No set amount of time is required for a longitudinal study, so long as the participants are repeatedly observed.
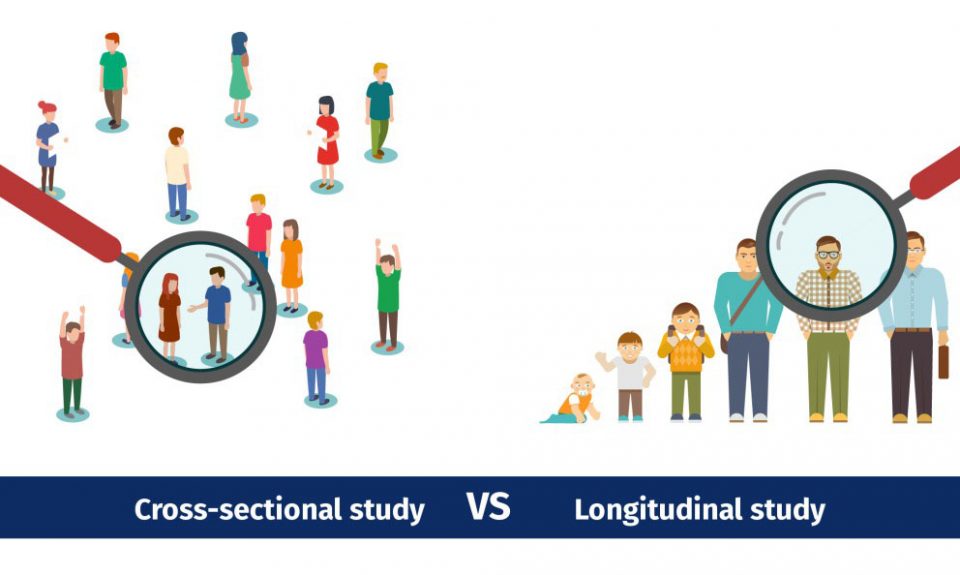
Unlike longitudinal studies, where the research variables can change during a study, a cross-sectional study observes a single instance with all variables remaining the same throughout the study. A longitudinal study may follow up on a cross-sectional study to investigate the relationship between the variables more thoroughly. Numerous variables are to be considered, and adequately controlled, when embarking on such a project. Additionally, the engagement and commitment of organisations contributing to the project is essential; and should be maintained and facilitated by means of regular training, communication and inclusion as possible. Conducting longitudinal research is demanding in that it requires an appropriate infrastructure that is sufficiently robust to withstand the test of time, for the actual duration of the study.
There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data. Retest effects refer to gains in performance that occur when the same or similar test is administered on multiple occasions. Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
That is really what drives us at Surveysparrow, that you might find something in the results you didn’t expect, and it might change the course of your company for the better. In this article, we’ll discuss the effects of selection bias, how it works, its common effects and the best ways to minimize it. A researcher wants to know if there’s any relationship between children who drink milk before school and high classroom performance. First, he uses a sampling technique to gather a large research population.
A 4-year longitudinal study investigating the relationship between flexible school starts and grades Scientific Reports - Nature.com
A 4-year longitudinal study investigating the relationship between flexible school starts and grades Scientific Reports.
Posted: Thu, 24 Feb 2022 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Famous Examples of Longitudinal Studies
Because the participants share the same genes, it is assumed that any differences are due to environmental analysis, but only an attentive study can conclude those assumptions. The design of the study is highly dependent on the nature of the research questions. Whenever a researcher decides to collect data by surveying their participants, what matters most are the questions that are asked in the survey.
All effort should be made to ensure maximal retention of participants; with exit interviews offering useful insight as to the reason for uncontrolled departures (3). Due to the length of the research process, some variables might be unable to complete the study for one reason or the other. Then, he conducts a baseline survey to establish the premise of the research for later comparison.
Advanced longitudinal methods such as cross-lagged panel modeling and growth curve modeling are reviewed. Finally, the advantages and disadvantages of conducting longitudinal research are outlined. Once researchers have determined the study's scope, participants, and procedures, most longitudinal studies begin with baseline data collection.
Let’s assume, for example, that you conduct an employee engagement survey every year. If your organization has done these surveys for the past 10 years, you now have more than enough material to conduct a retrospective study. You can then find out how employee engagement at your company has varied over time. A retrospective longitudinal study is when you take pre-existing data from previous online surveys and other research. The objective here is to put your results in a larger timeline and observe the variation in results over time.
One of the longest longitudinal studies, the Harvard Study of Adult Development, has been collecting data on the physical and mental health of a group of men in Boston, in the US, for over 80 years. Longitudinal studies are a type of correlational research in which researchers observe and collect data on a number of variables without trying to influence those variables. Both studies are valuable for psychologists to observe a given group of subjects. Still, cross-sectional studies are more beneficial for establishing associations between variables, while longitudinal studies are necessary for examining a sequence of events. There are many other techniques like latent transition analysis, event history analysis, and time series models that have specialized uses for particular research questions with longitudinal data. The choice of model depends on the hypotheses, timescale of measurements, age range covered, and other factors.
Without the cross-sectional study first, you would not have known to focus on men in particular. Both groups would then be observed over time to see if there are differences in outcomes, which could suggest an effect of the treatment or intervention. Case-control studies compare groups retrospectively and cannot be used to calculate relative risk. Longitudinal studies, though, can compare groups either retrospectively or prospectively. Detecting cohort effects is important but can be challenging as they are confounded with age and time of measurement effects. Techniques like maximum likelihood estimation and multiple imputation are better alternatives to older methods like listwise deletion.
During this time, the researcher can compare video game-playing behaviors with violent tendencies. Thus, investigating whether there is a link between violence and video games. Over many years, researchers can see both sets of twins as they experience life without intervention.